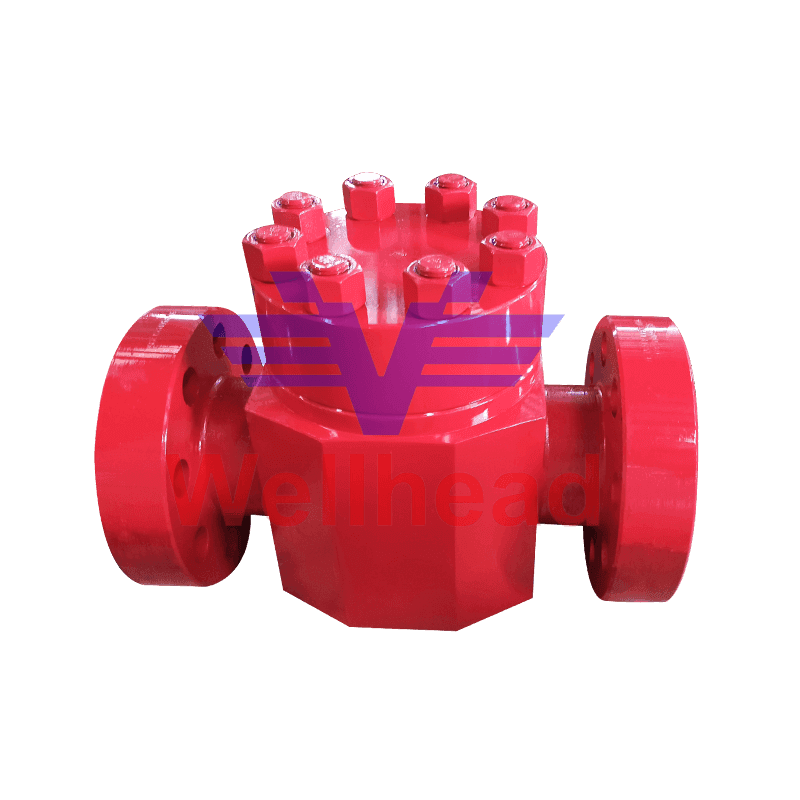
A High Pressure Plug Valve is a critical component in industrial piping systems, designed to regulate, start, or stop the flow of fluids under high-pressure conditions. Its robust construction and precise engineering make it suitable for oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and other demanding applications.
- 1. Overview of High Pressure Plug Valves
- 2. Main Specifications of High Pressure Plug Valves
- 3. Comparison with Other Valve Types
- 4. Applications of High Pressure Plug Valves
- 5. Advantages of High Pressure Plug Valves
- 6. Installation and Maintenance Tips
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: What pressure can a High Pressure Plug Valve handle?
- Q2: Can High Pressure Plug Valves be used for corrosive fluids?
- Q3: How does a plug valve compare with a ball valve for high-pressure use?
- Q4: What maintenance is required for these valves?
- Q5: Are High Pressure Plug Valves available in large diameters?
- 8. Conclusion
1. Overview of High Pressure Plug Valves
High Pressure Plug Valves operate by rotating a cylindrical or conically tapered plug within the valve body. The plug contains a passage that allows fluid flow when aligned with the pipeline and blocks flow when turned. The design ensures reliable sealing even in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Key Functions:
- Flow regulation: Allows partial or full flow control.
- Shut-off capability: Provides a reliable seal to stop fluid flow.
- Durability: Designed to handle extreme pressure and corrosive environments.
2. Main Specifications of High Pressure Plug Valves
The specifications of a High Pressure Plug Valve determine its performance, safety, and compatibility with different applications. Below are the most critical parameters:
2.1 Pressure Rating
High Pressure Plug Valves are engineered to withstand pressures ranging from 1500 psi up to 6000 psi or more, depending on the valve design and material. The pressure rating ensures safe operation in high-pressure pipelines.
2.2 Temperature Range
These valves can operate in extreme temperature environments. Standard ranges are -29°C to 425°C (-20°F to 800°F), while specialized designs using advanced alloys can handle even higher temperatures.
2.3 Materials of Construction
The choice of material is crucial for durability and corrosion resistance. Common materials include:
- Carbon Steel: Suitable for general high-pressure applications.
- Stainless Steel: Offers corrosion resistance in chemical or seawater applications.
- Alloy Steel: Provides high strength and temperature resistance.
- Bronze or Nickel Alloys: Used for specialized chemical or high-temperature pipelines.
2.4 End Connections
High Pressure Plug Valves are available with various end connections for easy installation:
- Threaded Ends: Suitable for smaller pipelines.
- Flanged Ends: Preferred for high-pressure and large-diameter pipelines.
- Butt Welded Ends: Provides a leak-proof connection for critical applications.
2.5 Valve Sizes
The valves come in sizes from ½ inch to 12 inches or larger, accommodating a wide range of flow requirements. Larger valves are typically custom-designed to meet industrial specifications.
2.6 Sealing Mechanisms
Reliable sealing is essential in high-pressure systems. Common sealing options include:
- PTFE Seats: Provide excellent chemical resistance.
- Metal-to-Metal Seats: Offer high-temperature and high-pressure durability.
- Elastomeric Seals: Used in low-temperature or lower-pressure applications.
2.7 Actuation Options
High Pressure Plug Valves can be manually operated or automated:
- Manual Lever or Gear Operated: For direct control in smaller systems.
- Pneumatic or Hydraulic Actuators: For automated control in larger or critical systems.
- Electric Actuators: Integrated with remote control systems for industrial automation.
3. Comparison with Other Valve Types
Understanding the differences between High Pressure Plug Valves and other valve types helps in selecting the right component for specific applications.
3.1 Gate Valve vs. High Pressure Plug Valve
- Operation: Gate valves require more space and time to operate, while plug valves provide quick quarter-turn operation.
- Sealing: Plug valves offer a tighter shut-off in high-pressure environments.
- Maintenance: Plug valves have simpler internal structures, reducing maintenance efforts.
3.2 Ball Valve vs. High Pressure Plug Valve
- Flow Control: Ball valves provide better flow capacity but may experience seat wear under abrasive fluids.
- Durability: Plug valves are more resistant to high-pressure erosion due to thicker plugs and metal-to-metal contact.
- Size Limitations: Plug valves are preferred for larger diameter, high-pressure pipelines.
4. Applications of High Pressure Plug Valves
High Pressure Plug Valves are versatile and used across various industries:
- Oil and Gas: Suitable for upstream, midstream, and downstream processes.
- Chemical and Petrochemical: Resistant to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures.
- Power Generation: Handling steam, cooling water, or other high-pressure fluids.
- Marine and Offshore: Used in seawater and high-pressure piping systems.
- Mining and Heavy Industry: Handling slurry, abrasive fluids, and other harsh environments.
5. Advantages of High Pressure Plug Valves
- Quick quarter-turn operation for fast control.
- Reliable sealing under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
- Durable construction requiring minimal maintenance.
- Versatile design suitable for corrosive and abrasive fluids.
- Compatibility with manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, and electric actuation.
6. Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance maximize valve performance and lifespan:
- Ensure alignment with pipeline to prevent stress on the valve body.
- Use appropriate torque when bolting flanged connections.
- Regularly inspect and lubricate the plug for smooth operation.
- Replace worn or damaged seals promptly to maintain pressure integrity.
- Consider automated actuation for valves in hard-to-reach or hazardous areas.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What pressure can a High Pressure Plug Valve handle?
Depending on the design and materials, these valves can handle pressures from 1500 psi up to 6000 psi or higher, making them suitable for extreme industrial applications.
Q2: Can High Pressure Plug Valves be used for corrosive fluids?
Yes, valves made from stainless steel, nickel alloys, or with specialized coatings are suitable for corrosive and chemical applications.
Q3: How does a plug valve compare with a ball valve for high-pressure use?
Plug valves offer thicker sealing surfaces and metal-to-metal contact, making them more resistant to erosion and more reliable in high-pressure, abrasive applications.
Q4: What maintenance is required for these valves?
Routine inspection, lubrication of the plug, and timely replacement of seals are essential. Manual valves may require less maintenance than automated actuated versions.
Q5: Are High Pressure Plug Valves available in large diameters?
Yes, they are available from ½ inch up to 12 inches and beyond. Custom designs are possible for even larger pipeline applications.
8. Conclusion
The High Pressure Plug Valve is a reliable, versatile, and durable solution for controlling fluid flow in demanding industrial applications. Its precise engineering, robust construction, and wide range of specifications make it an indispensable component in oil and gas, chemical, power, and heavy industries. When compared with other valve types, it offers quick operation, high sealing efficiency, and lower maintenance, ensuring long-term performance under extreme conditions.


 + 86-0515-88429333
+ 86-0515-88429333